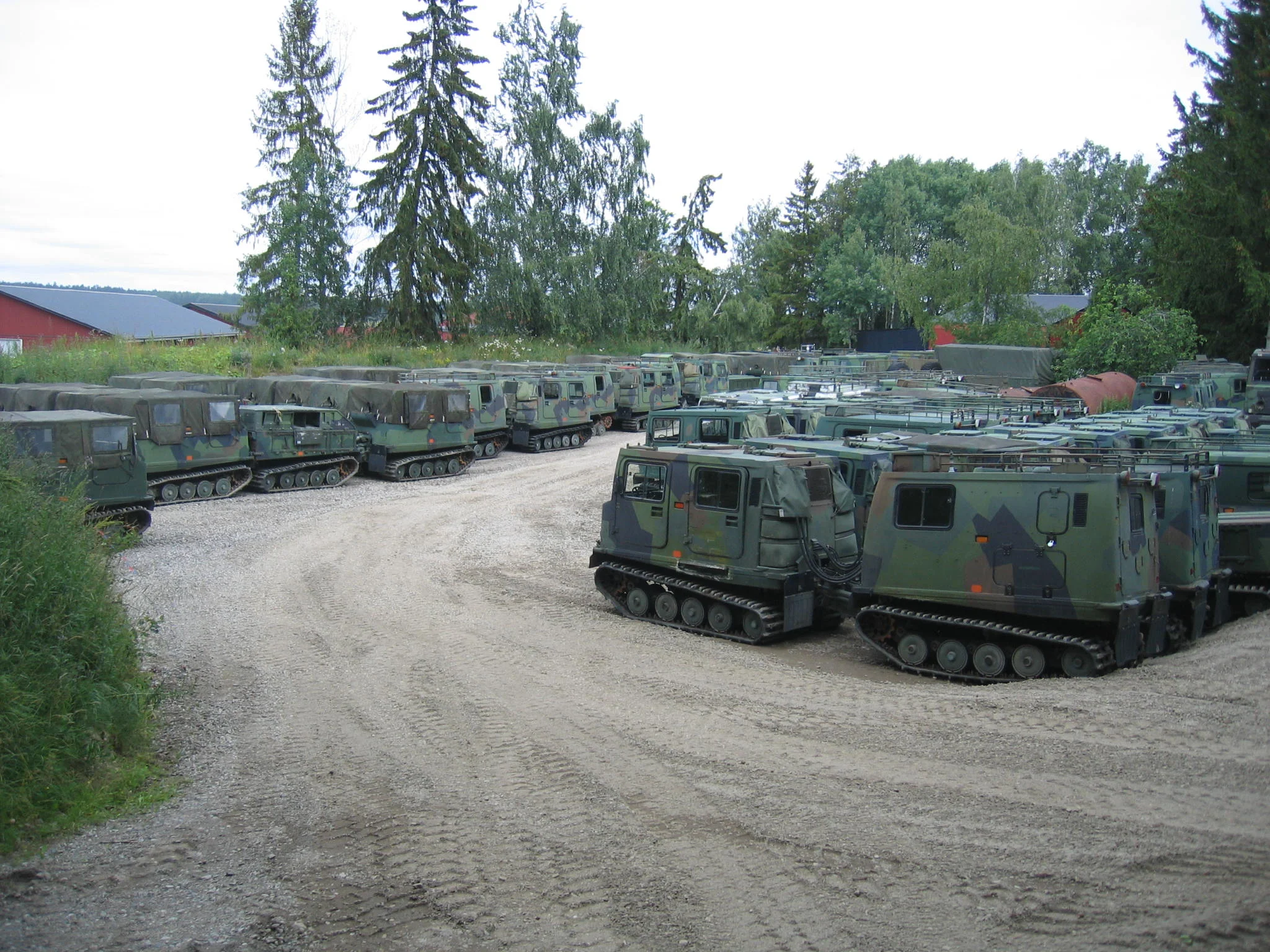
Bandvagn 206 is a tracked articulated, all-terrain carrier developed by Hägglunds. It consists of two units, with all four tracks powered. It can carry up to 17 people, 6 in the front compartment and 11 in the rear. The trailer unit can also be adapted for different applications.
The development of the Bv 206 all-terrain articulated tracked carrier began in 1974.
Three batches of trial vehicles were delivered between 1976 and 1978 and the first production examples were delivered to the Swedish Defense Administration in 1980.
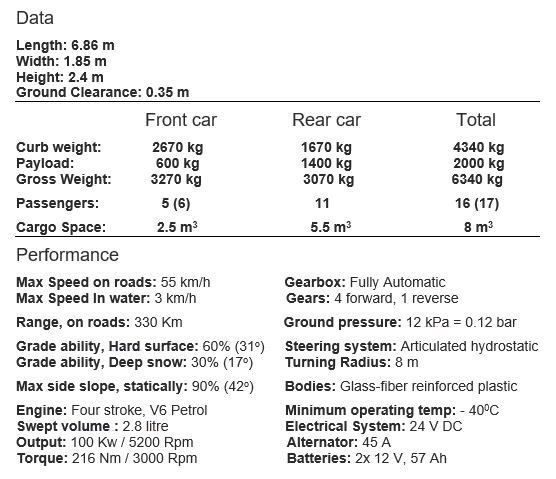
Like its predecessor, the Volvo Bv 202, the Bv 206 is designed to carry troops and equipment through snow and bog-lands in northern Sweden. The low ground pressure enables the Bv 206 to cope with a wide range of difficult conditions. It is also fully amphibious, with a speed in water of up to 4.7 km/h. Over 11,000 have been produced
and they are used in more than 37 countries worldwide.
The total load capacity is 2,250 kg and a trailer of up to 2,500 kg gross weight can also
be towed behind the second compartment.
The Bv 206 is referred to as a Small Unit Support Vehicle (SUSV) pronounced "susvee"
in United States service. U.S. military variants include the ambulance variant, the flat-bed cargo carrier, tactical operations center variant, and the standard model. U.S. military models are fitted with a 6-cylinder Mercedes diesel engine and a on-halon fire
suppression system since 1997 due to several cases where the front car caught fire
and burned to the frame.
Additional users are the American and Australian Antarctic research organizations and British, Icelandicand Canadian search and rescue services. They are also used for search and rescue services in the Australian alpine region. The Bv 206 was used in combat
by the Canadian Forces during Operation Anaconda. The Singapore Armed Forces
also uses the Bv 206 and recently transferred several of them to the Singapore Civil Defense Force to be used as a firefighting platform.
Decommissioned models have been purchased by private owners and rented as
transports, particularly in Alberta, Canada, in order to access remote oil wells,
as well as cut blocks which need to be reforested by tree planting.